Definition¶
What is an IPS?¶
An IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) is a network intrusion prevention system for protecting an organization's network(s). It is usually a specific hardware device that is integrated into the network topology to block and protect against intrusions. This is done by analyzing traffic for anomalies, specific signatures, or suspicious behaviors. For each type of detected intrusion, the system can decide whether the intrusion should be ignored, logged, an alert triggered to notify the incident response team, or directly blocked.
In summary, the goal of an IPS is to block traffic packets that are considered intrusions.
Comparison with IDS¶
- The goal of an IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is to detect intrusions and raise alerts without interfering with the organization's traffic, which means it will never block any packets, unlike an IPS.
- Additionally, an IDS can be configured in parallel with the topology, making its interposition optional. It probes the traffic mirrored from a port (mirror port or SPAN) to an interface of the system or the traffic circulating between two interfaces connected in a bridge (software switch).
- Like the IPS, the IDS can ignore the intrusion, log the incident, or trigger an alert. However, it cannot block traffic.
What is Redborder IPS?¶
The Redborder IPS can function as both an IPS and an IDS, depending on the operating mode and how it is integrated into the network topology. For brevity, we simply call it IPS in Redborder.
Basic Scenario for IPS Installation¶
A typical basic scenario proposed by the solution involves a set of sensors placed at various sensitive points in the organization's network, which will connect to a manager or cluster of managers for management and monitoring. These points consist of network links, called segments, through which sensitive traffic circulates and which the sensor will analyze more or less transparently, depending on the configured operating mode (IPS/IDS). For planning the installation of sensor equipment, some fundamental aspects should be considered:
- Bypass segments (paired specific network interfaces, usually with bypass support) will be interposed in the middle of the traffic to be analyzed.
- Management interfaces (in the form of bonding) for remote access from both normal equipment and the Manager.
- IPMI access interfaces for remote hardware management (SOL or Serial Over LAN connection, iKVM, and IPMI commands like start, restart, and shutdown). For the Manager, specific hardware is not required; the only condition is the existence of at least two network interfaces.
- This allows for the creation of a bonding for management and connection with the sensors and another bonding (optional) for communications to other networks. Both systems support the 802.1q standard for virtual LAN (optional when configuring).
If you have not installed the manager...
It is important to configure the Manager (or cluster of managers) before configuring and registering the first IPS sensor. The Manager must be operational and on a network accessible to the sensors. Some sensor configuration processes depend on access to the Manager. The installation scenario of the Redborder Manager is the same regardless of the sensors that are installed and registered (IPS, Flow, Malware (WIP), or Vault).
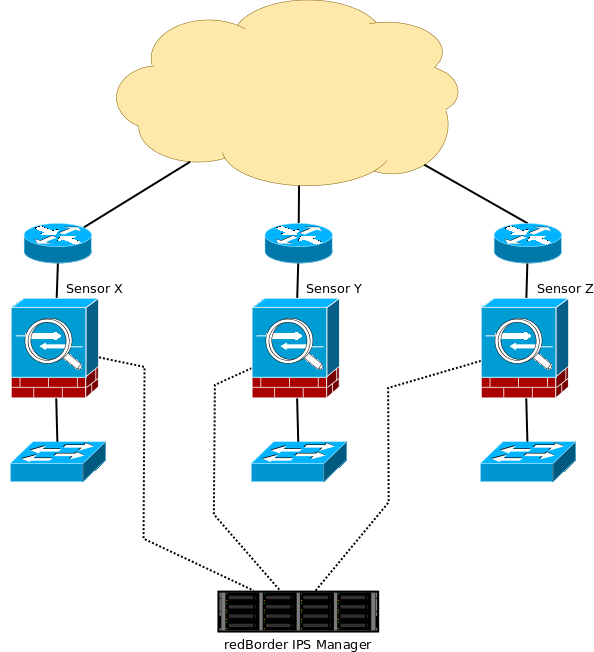
Basic Scenario for IPS Installation
User Interface Structure of the Installation Assistant¶
Initial Screen of the Installation Assistant
Option Selection¶
Navigating through our installation assistant is very simple:
- Move between the available options: press the arrow keys.
- Check a box: press the space key.
- Select an option: press the enter key.